The natural world, financial markets, and even the spread of information are often governed by a powerful, yet frequently misunderstood, principle: exponential growth. This concept describes a process where the rate of change itself increases over time, leading to surprisingly rapid and dramatic outcomes. Unlike linear growth, which adds the same amount in each period, exponential growth adds an amount proportional to the current quantity, creating a snowball effect that can quickly overwhelm expectations.
Unpacking the Basics of Exponential Growth
At its core, exponential growth is about multiplication. Imagine a quantity that doubles in size during a fixed period. Then, in the next period, it doubles again, but this time it doubles its *new*, larger size. This continuous multiplication is what gives exponential growth its characteristic accelerating curve.
Consider a simple scenario:
- Start with 1 unit.
- After Period 1, it doubles to 2 units.
- After Period 2, it doubles to 4 units.
- After Period 3, it doubles to 8 units.
The increase itself grows: from 1 to 2, then 2 to 4, then 4 to 8. This seemingly modest start can lead to astonishing numbers very quickly.
The Lily Pad Analogy: A Classic Illustration
One of the most famous examples to illustrate the counter-intuitive power of exponential growth involves a pond and a single lily pad. Imagine a pond where a single lily pad floats. This lily pad doubles in size every day. If it takes 30 days for the lily pads to completely cover the pond, how long does it take for the pond to be half-covered?
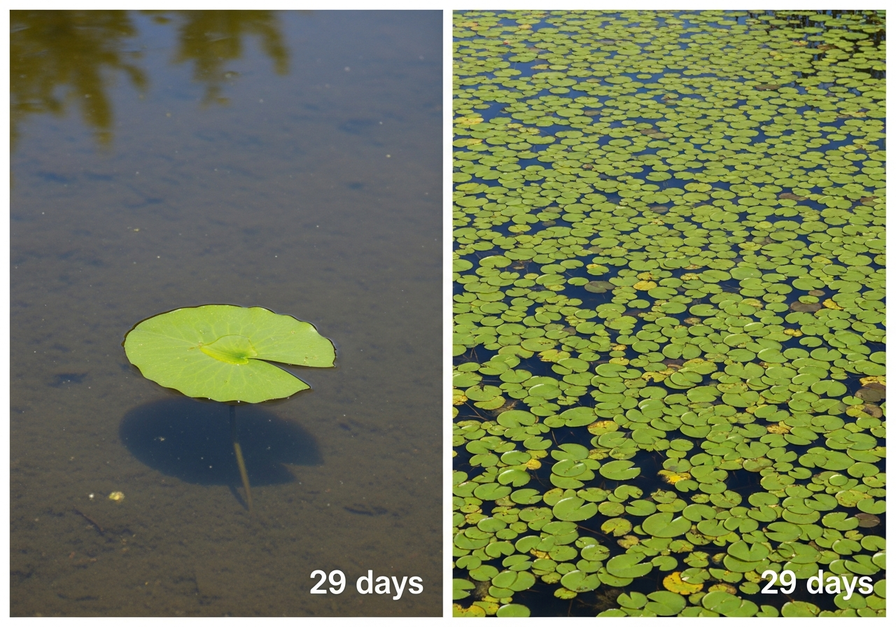

The answer often surprises people: it takes 29 days. On day 29, the pond is half-covered, and then on day 30, it doubles to become fully covered. This dramatic increase from one to many in just 29 days highlights how a small initial quantity can explode in size, often catching observers off guard until it is almost too late to react. This visual representation underscores the core lesson of exponential change.
Real-World Manifestations of Exponential Growth
The principle of exponential growth is not confined to theoretical lily pads. It plays a crucial role in many aspects of our world.
The Magic of Compound Interest
In finance, exponential growth is the engine behind compound interest. When an investment earns interest, and that interest itself begins to earn interest, the growth becomes exponential. A small initial sum can grow into a substantial fortune over time, given consistent returns and sufficient duration.
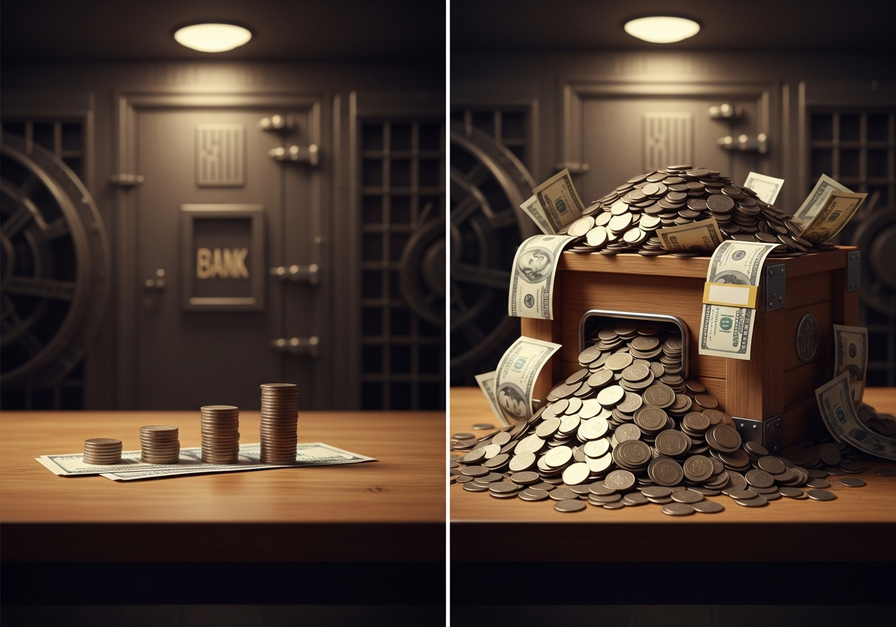

This illustration directly ties to the discussion of compound interest, showing how a modest start can grow exponentially, making the financial concept tangible and memorable. The longer the money is invested, the more pronounced the compounding effect becomes, demonstrating the power of time in financial growth.
Population Dynamics
Biological populations, whether of bacteria, insects, or humans, often exhibit exponential growth under ideal conditions. When resources are abundant and there are no limiting factors, a population can grow at an accelerating rate, as each new individual contributes to the reproductive capacity of the group. This is why understanding population growth is critical in ecology and resource management.
The Rapid Spread of Disease
The spread of infectious diseases is another stark example of exponential growth. One infected individual can transmit the pathogen to several others, who then each transmit it to more people, and so on. This chain reaction can quickly lead to an overwhelming number of cases.
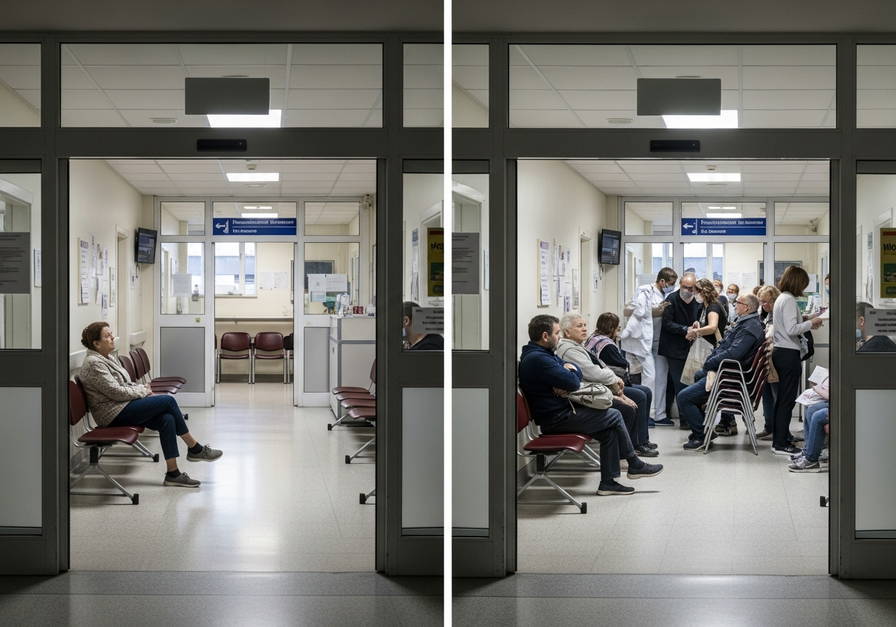
This photo demonstrates the real-world example of exponential growth in the spread of diseases. By contrasting a single patient with a crowded emergency department, it makes clear how quickly infection numbers can rise if unchecked, echoing the warning about the importance of early intervention and public health measures.
Technological Advancement
In the realm of technology, Moore’s Law, which posits that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years, is a famous example of exponential growth. This principle has driven the rapid advancement of computing power, leading to innovations that were unimaginable just a few decades ago.
The “J-Curve” and Its Inevitable Limits
Graphically, exponential growth is represented by a “J-curve,” a line that starts relatively flat and then shoots sharply upwards. This initial slow phase often lulls observers into a false sense of security, making the subsequent rapid acceleration even more surprising.
However, true exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely in any real-world system. Eventually, limiting factors come into play. For populations, these might include:
- Resource scarcity (food, water, space)
- Increased predation or disease
- Accumulation of waste products
When these limits are encountered, the growth rate slows down, and the curve transitions from a “J” shape to an “S” shape, known as logistic growth. This S-curve reflects a population stabilizing around the environment’s carrying capacity, the maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely.
Understanding the Mathematics of Exponential Growth
For those curious about the underlying mechanics, exponential growth can be described by a simple mathematical formula:
P(t) = P0 * (1 + r)t
Where:
- P(t) is the quantity after time t.
- P0 is the initial quantity.
- r is the growth rate (expressed as a decimal).
- t is the time period.
The key element here is ‘t’ in the exponent. This means that the quantity is multiplied by (1 + r) for each unit of time, leading to the accelerating growth. Even a small ‘r’ can lead to massive numbers over a long ‘t’.
Why Understanding Exponential Growth Matters
Grasping the concept of exponential growth is more than just an academic exercise; it is a vital tool for making informed decisions across various domains:
- Environmental Science: Predicting the impact of resource consumption or the spread of invasive species.
- Economics: Understanding long-term investment returns, national debt, or inflation.
- Public Health: Modeling disease outbreaks and planning interventions.
- Technology: Anticipating the pace of innovation and data proliferation.
Recognizing the early, seemingly insignificant stages of exponential growth allows for proactive measures, whether it is saving for retirement, implementing public health strategies, or managing ecological systems. Ignoring it can lead to situations where problems become unmanageable almost overnight.
Conclusion
Exponential growth is a fundamental force shaping our world, from the microscopic to the global scale. Its ability to transform small beginnings into overwhelming magnitudes is both a source of immense opportunity and significant challenge. By understanding its mechanics, recognizing its patterns, and appreciating its often counter-intuitive nature, individuals and societies can better navigate the complexities of growth and change, fostering sustainability and informed decision-making in an ever-evolving world.








